Buying Health Insurance?Everyone needs medical care sometime, and the most common way to pay for it is through private health insurance coverage. While most Americans have some type of private coverage, the different types of insurance and how they work can be confusing and difficult to understand.
When you need to purchase health insurance, turning to a local insurance agent or broker is always a smart first step. Whether you're looking at health, dental, disability or long-term care, your agent or broker will help you identify the benefits that will satisfy your individual needs or the needs of your company. They not only look out for your bottom line, but they also work to make sure you get the products that are right for you.
Expertise mattersProfessional health insurance agents and brokers provide the expertise you need to make the right choices. They are experts who:
- know the market - by distinguishing the best products from the merely adequate
- know the law - by reviewing state and federal legislation and regulations that impact the sale of health insurance products
- know the industry - by completing stringent licensing requirements and continuing education courses
Your health insurance agent will help you:- review your unique needs
- learn about different insurance companies and types of coverage that can satisfy your specific concerns
- ease the burden on your time by doing the "legwork" for you
- get the most from your coverage after you've bought it
Independent agents and brokers work for you--not any one insurance company. This ensures that your ongoing needs are their priority.
How can I buy individual health insurance coverage?In almost every state, individual health insurance coverage can be purchased through licensed health insurance salespeople known as agents or brokers. Independent agents and brokers sell insurance plans from many companies, and they can help you find the coverage that best suits your individual needs.
Agents and brokers also provide service on the policies they have sold, and can help you process claims or with anything else you need regarding your policy. The insurance companies for which agents and brokers sell coverage pay them a commission for their work, so you will not be charged a direct fee if you want to use the services of an agent or broker.
How is individual insurance different from group insurance?Individual health insurance is very different than group health insurance, which is the type of insurance that is offered through an employer. Since laws mandating what types of services must be included in individual policies are often different than those dictating what must be included in group policies, benefits are generally less extensive than what most people would receive through coverage they have through work. Individual consumers may be surprised to learn that some benefits that may be considered "standard" in a group policy, like maternity coverage or substance-abuse treatment, may not be included in an individual plan. Sometimes individual health insurance consumers have the option to pay extra for coverage such as accident or critical illness. This extra coverage is referred to as an optional rider.
Cost is often the primary factor for individual health insurance consumers, which is another reason why the benefits included in individual policies are often simpler. In addition, deductibles (the amount you have to pay before insurance benefits begin) and cost-sharing (the fees you pay directly to medical providers at the time of service) are also generally higher.
Individual health insurance companies are much more limited than group insurance companies in their ability to spread risk, so the laws concerning individual health insurance are different in most states.
How are premium rates determined?With Healthcare Reform, federal laws only allow carriers to rate a premium based on your age, where you live, how many to insure and if you use tobacco.
Are any pre-existing medical conditions covered?Yes, With Healthcare Reform, all pre-existing conditions are covered.
Can I still buy individual insurance if I have a very serious pre-existing medical condition?Yes. Same as above.
Questions to ask when choosing an individual health care planAsk friends and business associates what they do about health insurance. Put some thought into your needs and the needs of anyone else who will be included in the insurance plan. Do you or a dependent have any special health care needs to consider? Find out about each type of group insurance, mainly HMOs, PPOs, POSs, and Health Savings Accounts. When learning about each type of group insurance, compare whether you have a choice of doctors and how you would see a specialist, if needed.
- Find out if your location would rule out one of the types of group plans.
- Find out if there are enough health care providers close to you for the group network you are considering.
- Think about any extra services you might need, such as therapy or equipment, and whether they are covered medical services.
- Find out if a prescription plan comes with the group policy.
Note if one policy has more exclusions on medical services than the other. You may choose one type over another based on these exclusions and the comparative price of the premiums. Find out how each plan deals with a possible dispute over a benefit. Find out about individual health insurance, not forgetting that it is more expensive than group coverage. Sometimes individual insurance is your only option.
What is the first thing I should know about buying health coverage?Your aim should be to insure yourself and your family against the most serious and financially disastrous losses that can result from an illness or accident. If you are offered health benefits at work, carefully review the plans' literature to make sure the one you select fits your needs. If you purchase individual coverage, buy a policy that will cover major expenses and
pay them to the highest maximum level. Save money on premiums, if necessary, by
taking large deductibles and paying smaller costs out-of-pocket.
What should I look for? Although everyone's individual needs are different, there are key factors that you should look at when making a fully informed choice for one plan over another. Here are several key questions you should ask yourself when looking over your healthcare options.
When looking over your healthcare options, ask yourself:
- How all-inclusive do I want coverage of healthcare services to be?
- How much am I willing to spend on premiums?
- What type of healthcare plan is this, ie. a medical discount plan, limited benefit plan, or a
full featured plan?
- Is it a group plan or an individual health insurance policy?
- Is this plan considered to be continuous credible coverage under HIPAA?
Major Medical Plans vs Limited Benefit PlansMajor medical plans are a special type of
fee-for-service plan. They are designed to provide protection against long-term chronic or catastrophic illness or injury. These plans cover a broad area of health care services and are designed to protect against large medical expenses only. Typically included in a major medical plan are:
- the services of private registered nurses
- at-home, in-office, and in-hospital medical care
- X-ray treatment
- prescription drugs
- laboratory tests
Advantages of major medical plans.Despite the high deductible and the possible coinsurance requirement, major medical plans have several advantages over basic benefit plans:
- Instead of covering only certain enumerated expenses, major medical plans cover all personal medical expenses (with a few exceptions) whether incurred in or out of a hospital. Major medical plans are, therefore, more fair because they reimburse virtually all patients according to the same formula, regardless of the specialties of the attending physician, the location of the treatment, the drug treatment used, or the diagnostic techniques employed.
- Unlike many basic plans, major medical plans do not encourage unnecessary or prolonged hospitalization by covering medical service only if it is rendered in a hospital.
- The maximum amount of benefits payable is much higher under a major medical plan than under a basic medical plan, particularly in the areas of physician and surgeon fees.
- Partially reimbursing medical expenses has the combined effect of having a deductible and coinsurance in major medical plans and has three advantages over basic plans that provide full reimbursement:
- It discourages over-utilization of services and unnecessarily expensive treatment and facilities - both of which raise costs for you and your employees.
- It gives plan participants an incentive to police their own medical fees and keep costs down.
- It eliminates the payment of many small claims, thereby reducing administrative costs and saving money that would otherwise be spent on higher premiums to offset the additional administrative costs.
Types of major medical. There are two types of major medical plans: comprehensive plans that coinsure all covered medical expenses exceeding the deductible and supplementary plans that coinsure expenses in excess of the deductible and expenses in excess of those covered by another plan. Both supplementary plans and comprehensive plans place ceilings on the amount of benefits payable for each insured person.
Comprehensive plans. Comprehensive major medical plans provide coverage for the same types of services covered many other plans. Comprehensive plans also include deductibles and copayment requirements but may provide first-dollar coverage (full coverage with no deductible) for emergency accident benefits or waive out-of-pocket expenses for certain benefits.
Supplemental plans. These plans act as a supplement to another health insurance plan. Supplemental major medical plans cover most medically necessary services excluded under basic insurance plans, as well as charges that exceed the primary plan's limits. Covered services typically include inpatient and outpatient hospital care, special nursing care, outpatient prescription drugs, medical appliances, durable medical equipment, and outpatient psychiatric care. Supplemental major medical plans set deductibles, require copayments, and often limit total benefits.
Who will like major medical plans? Major medical plans may be popular with low-wage earners if they are healthy because the cost is lower than some other, more comprehensive plans. In fact, the premiums are usually lower than they would be with an HMO. Low-wage earners with health problems will not like them because of the deductibles involved.
Mini-meds. These mini-policies will pay you a fixed amount for every service you receive, regardless of how much that service actually costs. For example, if your mini-med pays $200 a day for hospitalization, that's how much you will receive even if your stay costs $400 a day. On the positive side, you will be able to choose your doctor and hospital.
Mini-meds can cost as little as $40 a month, but limit the amount of times they'll pay for a specific benefit that year. For example, a plan might pay $50 per visit for five children's visits or up to $1,000 per hospital stay.
In keeping with their low premiums, mini-meds generally limit yearly benefits to between $1,000 to $10,000. Services vary widely, so be sure to ask exactly what would be covered if you're considering this option.
Some mini-med plans give discounts on some services such as dental, chiropractic care, or prescription drugs instead of covering them. Others may have a monthly allowance for prescription drugs, a health care hotline, or discounts at a health club. Still others may allow you to purchase supplemental coverage for services such as maternity care or critical illness coverage for specified conditions.
Advantages - Low cost and likely no deductible
- Often offers coverage to people with pre-existing conditions
- Can save young, healthy people money if no major medical care is needed
- Can provide supplemental coverage when used in combination with a full insurance plan
Disadvantages - Does not cover your costs if you become seriously ill or hurt
- If you get sick while you have a limited benefit plan and want to purchase a comprehensive major medical plan, you will likely be denied coverage due to your pre-existing condition.
- Provides less coverage than other options such as high-deductible health plans and government programs
Questions to ask when choosing an individual health care planAsk friends and business associates what they do about health insurance. Put some thought into your needs and the needs of anyone else who will be included in the insurance plan. Do you or a dependent have any special health care needs to consider? Find out about each type of group insurance, mainly HMOs, PPOs, POSs, and Health Savings Accounts. When learning about each type of group insurance, comparewhether you have a choice of doctors and how you would see a specialist, if needed.
Note if one policy has more exclusions on medical services than the other. You may choose one type over another based on these exclusions and the comparative price of the premiums. Find out how each plan deals with a possible dispute over a benefit. Find out about individual health insurance, not forgetting that it is more expensive than group coverage. Sometimes individual insurance is your only option.
Make a comparison chart of your two final choices, listing the different costs of each of the following: - Deductible for each individual
- Deductible total for the family
- Deductible for out-of-network providers (if different)
- Co-payment
- After deductible is met, percentage of fees paid by insurance company for network providers
- After deductible is met, percentage of fees paid by insurance company for out-of-network providers
- Maximum limit insurance will pay for each claim
- Maximum limit insurance will pay over one's lifetime
- Uncovered medical expenses that will be out-of-pocket
- Can I afford the annual costs
What types of plans are available?PPO's - the most common type of plan in the states of Kansas and Missouri. Managed Care plans such as;
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs) allow the insured to choose medical providers that may or may not be a part of the network. If you decide to use a doctor within the PPO network, you will be responsible for a copayment. If you go outside the network you are responsible for a larger percentage of the costs.
Indemnity insurance - Once you meet your deductible, most indemnity plans pay a portion of what is considered appropriate charges for covered services. The usual split ofhow much the insurer and insured pays is 80/20. You are responsible for the 80 percent and the insurance company pays the remaining 20 percent. The policy will also cover charges for lab and x-rays, prescriptions as well as care from doctors and hospitals.
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) offer members a variety of health benefits for a set monthly fee. HMOs provide you with a list of doctors from their network so that you can choose a primary care physcian (PCP). When you have chosen your PCP, they will be the core of providing your medical needs. If you were to need a specialist you would first need to obtain a referral from your PCP. If you were to go to a physician outside of the network you would be responsible for the charges, unless of course you or a family member is in an emergency situation.
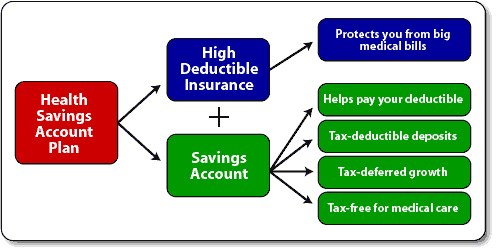
What is a High Deductible Health Plan?A high deductible health plan, often called consumer driven insurance, is a health plan with lower premiums and a higher deductible for major care, like a hospitalization or surgery. At the same time someone enrolls in a high deductible plan, he or she may also need to enroll in a health savings account (HSA). Generally, the person may put up to the amount of the deductible from income into this account, and the money is not taxed. Deductibles vary from as low as 1000 US dollars (USD) for an individual, to several thousand USD for family or couple coverage.
Basically it is health insurance that covers you for unusual and catastrophic illness and injury. What that means is, don.t expect to see any money or co-pays when you do your usual yearly thing - annual exams, yearly tests, trip to the doctor for the flu, etc. But, if you have an unexpected situation in any given year or acquire a chronic or acute condition (major injury, cancer, heartdisease, sudden hospitalization or surgeries) you are covered. Essentially you are using insurance for its original intent - to protect yourself against major financial woes.
What is a HSA-Qualified High Deductible Health Plan?Health Savings Account (HSA) qualified Health Plans or High Deductible Health Plans (HDHP) are now available from most insurance companies. These plans were designed to offer a tax incentive for qualified health related expenses while utilizing a High Deductible Health Plan with lower premiums. These plans are regulated by The US Department of the Treasury and require a minimum per person or family deductible.
An HSA qualified HDHP must be established before you can open and contribute to a Health Savings Account. Before any benefits can be paid under one of these plans, the per person or per family deductible would have to be met first. Therefore all medical expenses and prescription drug amounts covered by the plan would be applied toward meeting the deductible first. However, plans may allow for certain "preventative care" expenses to be paid on a first-dollar basis. Once the deductible has been met, benefits as outlined by the policy would begin.
What is an HSA?An HSA works like an IRA, except that money is used to pay health care costs. Participants enroll in a relatively inexpensive high deductible insurance plan. Then, a tax-deductible savings account may be opened to cover current and future medical expenses. The money deposited, as well as the earnings, is tax-deferred. The money can then be withdrawn to cover qualified medical expenses tax-free. Unused balances roll over from year to year.
Everyone (not just the self-employed or small businesses) with a qualified high deductible insurance plan is eligible for a tax-deductible HSA.
And how does an HSA work?You obtain coverage under a qualified health insurance plan with a minimum deductible of $1,100 for ingles and $2,200 for families. You are then allowed to deposit up to $2,900 for singles or $5,800 for families into your Health Savings Account for 2008. Older Americans can save even more. You do not have to itemize your deductions on your federal income taxes to deduct your contributions to an HSA. You can use the savings account to pay for your lower-dollar medical expenses, or those that are not covered by the health plan. Once you meet the deductible, the health insurance covers your medical expenses as defined in the policy.